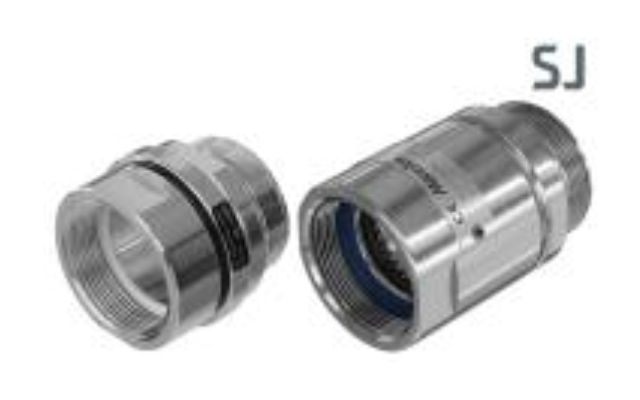

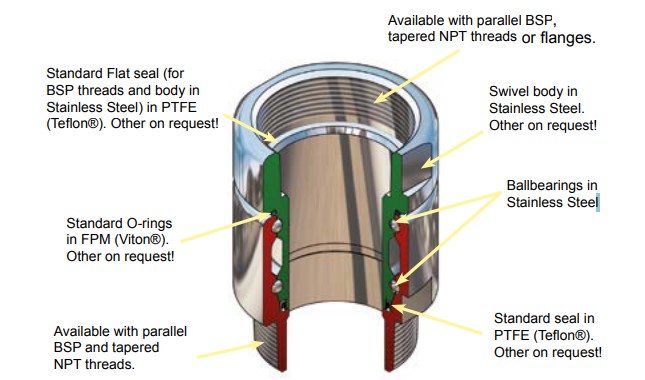
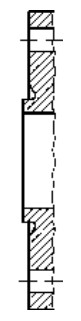
Swivel Joints

Swivel Joints are used in the industry wherever a movable pipe-connection system between two equipment parts is needed. Avoiding one of the biggest causes of premature hose failure. Torque stress is the largest single cause of PTFE and Stainless steel convoluted hose failure.
The swivel joints are designed for slow rotary motions under the influence of high internal pressures and/or external stress such as traction and bending forces.
With an appropriate combination of swivel joints nearly all movements from the simple rotation or swivelling motion up to motional actions in space can be realized.
The use of hose swivels avoids torsion of hose assemblies, i.e. in filling machines, and improves the handling and coupling of nozzles for refuelling of petroleum based products and chemicals.

NOTE
Unsuitable for high bending moments. Heavy Duty Swivels should be used in these applications.
Low maintenance
Each unit consist of two body halves. Stainless Steel balls and a single spring assisted O-ring seal.
Compact external dimensions
High flow rate / low pressure drop
Full range of sizes, materials, seals and connections
Minimal maintenance requirements
Safety
Swivel function - allows the hose to relax to it´s natural rest position whilst allowing freedom of movement without imparting torque stress at the point of connection - Torque stress is the largest single cause of Composite, PTFE and Stainless Steel convoluted hose failure.
Economical
Cost effective solution to prolong lifetime of hoselines.

Combinations of sizes, connections and materials
| Swivel maten |
|
3/4” |
1” |
1 1/4” |
1 1/2” |
2” |
2 1/2” |
3” |
4” |
|
Threads (Female / Male1)) |
|
BSP (ISO 228) |
|
NPT (ASME/ANSI 1.20.1 |
|
BSPT (EN 10226) |
|
ACME |
|
Weld end |
|
Flanges |
|
DIN Flange (ISO 1092 PN 10/16, PN 25/40 (Type A, B, E, F 2) ) |
|
ASA Flange (ASME/ANSI 16.5) |
|
TW-Flange (DIN 28459) |
|
T.T.M.A |
1) Any combinations of male and female threads is possible.
2) Se page14 for illustrations of different types of DIN-flanges.
| Standard materials and standard seals |
| Component | Material | Material standard | Operation temp | O-ring | Flat seal |
| Body |
Aluminium
Brass
Stainless Steel |
EN 755 - AW-6262-T6 EN 1706-AC-42100-T6 EN 12164 - CW614N EN 1982 - CB491K-GS EN 10272 - 1.4404+AT EN 10213 - 1.4409+AT |
-40oC to 250oC |
FPM/KFM (Viton®) |
PUR (Vulkollan®)
PUR (Vulkollan®)
PTFE (Teflon®) |
Working Pressure: (10 bar) - 300 psi (20 bar)
We manufacture Swivels in different sizes, connections and materials on request!
| One side | Other side |
| BSP/NPT Female | BSP/NPT Female |

| One side | Other side |
| BSP/NPT Female | BSP/NPT Male |

| One side | Other side |
| BSP/NPT Male | BSP/NPT Male |

| One side | Other side |
| BSP/NPT Thread | Flange |

| One side | Other side |
| Flange | Flange |

| One side | Other side |
| Weld end | Weld end *) |

The swivel Heavy duty is designed especially for hose rails to load and unload products like Aliphatic and Aromatic hydrocarbons, Alcohols and Amines, Ether and Ester, Glycos and Water, Liquid Fertilizers, Acids and Lyes.
NOTE
Please ask us for your special application.
• Offshore hose reels ship-to-shore
• Oil platform loading rigs
• Marine and industrial loading arms
• Hoses for road and rail tanker
• Chemical and petrochemical liquids
and liquefied gases.

Low maintenance
Each unit consist of two body halves. Stainless Steel balls and a single spring assisted O-ring seal.
Compact external dimensions
High flow rate / low pressure drop
Full range of sizes, materials, seals and connections
Minimal maintenance requirements
Safety
Swivel function - allows the hose to relax to it´s natural rest position whilst allowing freedom ofmovement without imparting torque stress at thepoint of connection - Torque stress is the largestsingle cause of Composite, PTFE and Stainless Steel convoluted hose failure.
Economical
Cost effective solution to prolong lifetime of hoselines.
Combinations of sizes, connections and materials
| Swivel sizes |
|
2" |
3" |
4" |
5" |
6” |
8" |
10" |
|
Threads (Female / Male1)) |
|
BSP (ISO 228) |
|
NPT (ASME/ANSI 1.20.1 |
|
BSPT (EN 10226) |
|
ACME |
|
Victaulic |
|
Weld end |
|
Flanges |
|
DIN Flange (ISO 1092 PN 10/16, PN 25/40 (Type A, B, E, F 2) ) |
|
ASA Flange 150 psi / 300 psi (ASME/ANSI 16.5) |
|
TW-Flange (DIN 28459) |
|
T.T.M.A |
1) Any combinations of male and female threads is possible.
2) Se page 14 for illustrations of different types of DIN-flanges
| Standard materials and standard seals |
| Component | Material | Material standard | Operation temp | Seal | Flat seal |
| Body |
Aluminium
Stainless Steel |
EN 755 - AW-6262-T6 EN 1706-AC-42100-T6 EN 10272 - 1.4404+AT EN 10213 - 1.4409+AT |
-100oC to 250oC |
PTFE (Teflon®) |
PUR (Vulkollan®)
PTFE (Teflon®) |
Working Pressure: 150 psi (10 bar)-1800 psi (125 bar)
We manufacture Swivels in different sizes, connections and materials on request!
| one side | Other side |
| BSP/NPT F | BSP/NPT F |
| One side | Other side |
| BSP/NPT F | BSP/NPT M |

| One side | Other side |
| BSP/NPT M | BSP/NPT M |

| One side | Other side |
| Thread | Flange |
| One side | Other side |
| Flange | Flange |

| One side | Other side |
| Victaulic | Victaulic*) |

| One side | Other side |
| Weld end | Weld end *) |

| Compact version |

NOTE
For loading arm applications, contact our technical department
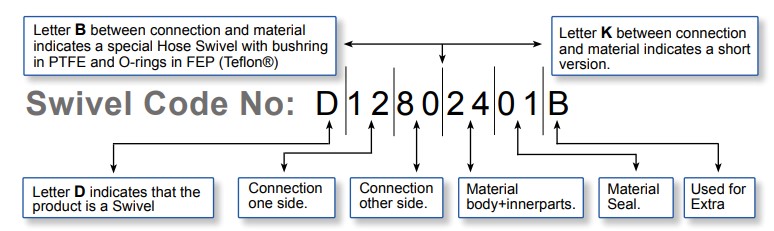
Connections (thread, flange etc.)
O-ring / Seals materials

Used for extra (last letter)
A = Flat Seal, PTFE (Teflon®)
B = Flat Seal PUR (Vulkollan®)
D = Flat Seal FPM (Viton®)
W = Double Ball Race
E.G. Code No: D10794401A=Hose Swivel, Single ball bearing
One side: 2" BSP (Female) Other side: 2" NPT (Male)
Material: Stainless Steel, Flat Seal PTFE (Teflon®)
E.G. Code No: D85614401W=Swivel, Double ball race
One side: 4" NPT (Male) Other side: Flange 3", ANSI (ASA) 150 psi
Material: Stainless Steel
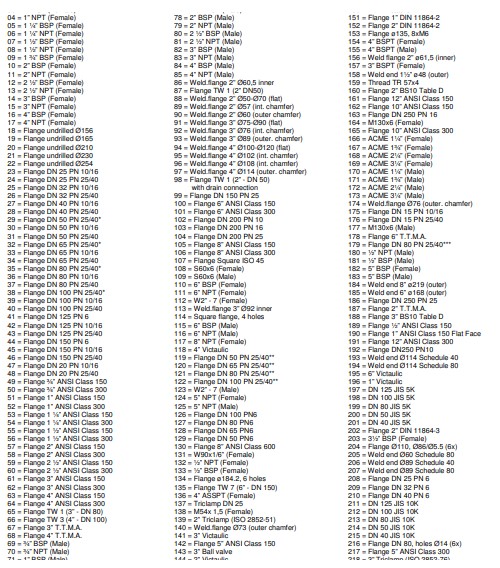
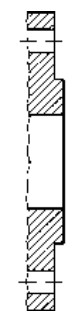
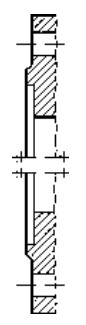
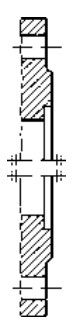
Type A Flat face Type B Raised face Type C Tongue Type D Groove
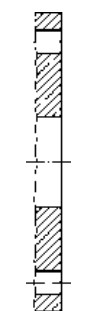
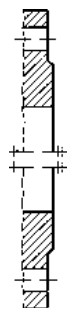
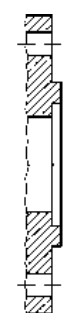
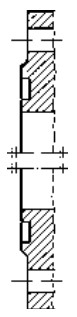
Type E Spigot Type F Recess Type G O-ring Spigot Type G O-ring Groove
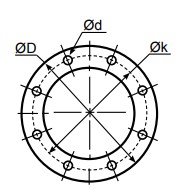
Ø D = Diameter
Ø k = Centre diameter
n = Numer of holes
Ø d = Hole diameter
|
EN 1092-1 |
|
DN |
PN 10 |
PN 16 |
PN 25 |
PN 40 |
||||||||||||
|
ØD |
Øk |
n |
Ød |
ØD |
Øk |
n |
Ød |
ØD |
Øk |
n |
Ød |
ØD |
Øk |
n |
Ød |
|
|
20 |
mm 105 |
75 |
4 |
14 |
105 |
75 |
4 |
14 |
105 |
75 |
4 |
14 |
105 |
75 |
4 |
14 |
|
|
inch 4.13 |
2.95 |
0.55 |
4.13 |
2.95 |
0.55 |
4.13 |
2.95 |
0.55 |
4.13 |
2.95 |
0.55 |
||||||
|
25 |
mm |
115 |
85 |
4 |
14 |
115 |
85 |
4 |
14 |
115 |
85 |
4 |
14 |
115 |
85 |
4 |
14 |
|
inch |
4.53 |
3.35 |
0.55 |
4.53 |
3.35 |
0.55 |
4.53 |
3.35 |
0.55 |
4.53 |
3.35 |
0.55 |
|||||
|
32 |
mm |
140 |
100 |
4 |
18 |
140 |
100 |
4 |
18 |
140 |
100 |
4 |
18 |
140 |
100 |
4 |
18 |
|
inch |
5.51 |
3.94 |
0.71 |
5.51 |
3.94 |
0.71 |
5.51 |
3.94 |
0.71 |
5.51 |
3.94 |
0.71 |
|||||
|
40 |
mm |
150 |
110 |
4 |
18 |
150 |
110 |
4 |
18 |
150 |
110 |
4 |
18 |
150 |
110 |
4 |
18 |
|
inch |
5.91 |
4.33 |
0.71 |
5.91 |
4.33 |
0.71 |
5.91 |
4.33 |
0.71 |
5.91 |
4.33 |
0.71 |
|||||
|
50 |
mm |
165 |
125 |
4 |
18 |
165 |
125 |
4 |
18 |
165 |
125 |
4 |
18 |
165 |
125 |
4 |
18 |
|
inch |
6.50 |
4.92 |
0.71 |
6.50 |
4.92 |
0.71 |
6.50 |
4.92 |
0.71 |
6.50 |
4.92 |
0.71 |
|||||
|
65 |
mm |
185 |
145 |
4 |
18 |
185 |
145 |
4 |
18 |
185 |
145 |
8 |
18 |
185 |
145 |
8 |
18 |
|
inch |
7.28 |
5.71 |
0.71 |
7.28 |
5.71 |
0.71 |
7.28 |
5.71 |
0.71 |
7.28 |
5.71 |
0.71 |
|||||
|
80 |
mm |
200 |
160 |
8 |
18 |
200 |
160 |
8 |
18 |
200 |
160 |
8 |
18 |
200 |
160 |
8 |
18 |
|
inch |
7.87 |
6.30 |
0.71 |
7.87 |
6.30 |
0.71 |
7.87 |
6.30 |
0.71 |
7.87 |
6.30 |
0.71 |
|||||
|
100 |
mm |
220 |
180 |
8 |
18 |
220 |
180 |
8 |
18 |
235 |
190 |
8 |
22 |
235 |
190 |
8 |
22 |
|
inch |
8.66 |
7.09 |
0.71 |
8.66 |
7.09 |
0.71 |
9.25 |
7.48 |
0.87 |
9.25 |
7.48 |
0.87 |
|||||
|
125 |
mm |
250 |
210 |
8 |
18 |
250 |
210 |
8 |
18 |
270 |
220 |
8 |
26 |
270 |
220 |
8 |
26 |
|
inch |
9.84 |
8.27 |
0.71 |
9.84 |
8.27 |
0.71 |
10.63 |
8.66 |
1.02 |
10.63 |
8.66 |
1.02 |
|||||
|
150 |
mm |
285 |
240 |
8 |
22 |
285 |
240 |
8 |
22 |
300 |
250 |
8 |
26 |
300 |
250 |
8 |
26 |
|
inch |
11.22 |
9.45 |
0.87 |
11.22 |
9.45 |
0.87 |
11.81 |
9.84 |
1.02 |
11.81 |
9.84 |
1.02 |
|||||
|
200 |
mm |
340 |
295 |
8 |
22 |
340 |
295 |
12 |
22 |
360 |
310 |
12 |
26 |
375 |
320 |
12 |
30 |
|
inch |
13.39 |
11.61 |
0.87 |
13.39 |
11.61 |
0.87 |
14.17 |
12.20 |
1.02 |
14.76 |
12.60 |
1.18 |
|||||
|
250 |
mm |
395 |
355 |
12 |
22 |
405 |
355 |
12 |
26 |
425 |
370 |
12 |
30 |
450 |
385 |
12 |
33 |
|
inch |
15.55 |
13.98 |
0.87 |
15.94 |
13.98 |
1.02 |
16.73 |
14.57 |
1.18 |
17.72 |
15.16 |
1.30 |
|||||
|
300 |
mm |
445 |
400 |
12 |
22 |
460 |
410 |
12 |
26 |
485 |
430 |
16 |
30 |
515 |
450 |
16 |
33 |
|
inch |
17.52 |
15.75 |
0.87 |
18.11 |
16.14 |
1.02 |
19.09 |
16.93 |
1.18 |
20.28 |
17.65 |
1.30 |
|||||
|
EN 1092-1 EN 1092-1 PN 6 |
DIN. |
|
DIN 2631 |
|
|
EN 1092-1 PN 10 |
DIN 2632 |
|
EN 1092-1 PN 16 |
DIN 2633 |
|
EN 1092-1 PN 25 |
DIN 2634 |
|
EN 1092-1 PN 40 |
DIN 2635 |
|
EN 1092-1 Type B Raised Face |
DIN 2526 Form C |
|
EN 1092-1 Type C Tongue |
DIN 2512 Form F |
|
EN 1092-1 Type D Groove |
DIN 2512 Form N |
|
EN 1092-1 Type E Spigot |
DIN 2513 Form V |
|
EN 1092-1 Type F Recess |
DIN 2513 Form R |
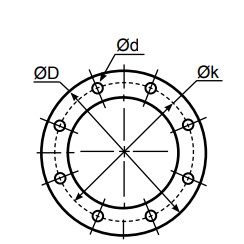
Ø D = Diameter
Ø k = Centre diameter
n = Numer of holes
Ø d = Hole diameter
|
ANSI (ASA) B 16,5 |
|
INCH |
150 psi |
300 psi |
||||||
|
ØD |
Øk |
n |
Ød |
ØD |
Øk |
n |
Ød |
|
|
3/4” |
mm |
98,4 |
69,8 |
4 |
15,9 |
117,5 |
82,5 |
4 |
19 |
|
inch |
3 7/8 |
2 3/4 |
5/8 |
4 5/8 |
3 1/4 |
3/4 |
|||
|
1” |
mm |
107,7 |
79,4 |
4 |
15,9 |
123,8 |
88,9 |
4 |
19 |
|
inch |
4 1/4 |
3 1/8 |
5/8 |
4 7/8 |
3½ |
3/4 |
|||
|
1 1/4” |
mm |
117,5 |
88,9 |
4 |
15,9 |
133,3 |
98,4 |
4 |
19 |
|
inch |
4 5/8 |
3½ |
5/8 |
5 1/4 |
3 7/8 |
3/4 |
|||
|
1 1/2” |
mm |
127 |
98,4 |
4 |
15,9 |
155,6 |
114,3 |
4 |
22,2 |
|
inch |
5 |
3 7/8 |
5/8 |
6 1/8 |
4½ |
7/8 |
|||
|
2” |
mm |
152,4 |
120,6 |
4 |
19 |
165,1 |
127 |
8 |
19 |
|
inch |
6 |
4 3/4 |
3/4 |
6½ |
5 |
3/4 |
|||
|
2 1/2” |
mm |
177,8 |
139,7 |
4 |
19 |
190,5 |
149,2 |
8 |
22,2 |
|
inch |
7 |
5½ |
3/4 |
7½ |
5 7/8 |
7/8 |
|||
|
3” |
mm |
190,5 |
152,4 |
4 |
19 |
209,5 |
168,3 |
8 |
22,2 |
|
inch |
7½ |
6 |
3/4 |
8 1/4 |
6 5/8 |
7/8 |
|||
|
4” |
mm |
228,5 |
190,5 |
8 |
19 |
254 |
200 |
8 |
22,2 |
|
inch |
9 |
7½ |
3/4 |
10 |
7 7/8 |
7/8 |
|||
|
5” |
mm |
254 |
215,9 |
8 |
22,2 |
279,4 |
234,9 |
8 |
22,2 |
|
inch |
10 |
8½ |
7/8 |
11 |
9 1/4 |
7/8 |
|||
|
6” |
mm |
279,4 |
241,3 |
8 |
22,2 |
317,5 |
269,9 |
12 |
22,2 |
|
inch |
11 |
9½ |
7/8 |
12½ |
10 5/8 |
7/8 |
|||
|
8” |
mm |
342,9 |
298,4 |
8 |
22,2 |
381 |
330,2 |
12 |
25,4 |
|
inch |
13½ |
11 3/4 |
7/8 |
15 |
13 |
1 |
|||
|
10” |
mm |
406,4 |
361,9 |
12 |
25,4 |
444,5 |
387,3 |
16 |
28,6 |
|
inch |
16 |
141/4 |
1 |
17½ |
15 1/4 |
1 1/8 |
|||
|
12” |
mm |
482,6 |
431,8 |
12 |
25,4 |
520,7 |
450,8 |
16 |
31,7 |
|
inch |
19 |
17 |
1 |
20½ |
17 3/4 |
1 1/4 |
|
TW DIN 28459 |
|
|
DN |
ØD |
Øk |
n |
Ød |
|
TW1 |
50 |
mm |
154 |
130 |
8 |
11 |
|
inch |
6.06 |
5.12 |
|
0.43 |
||
|
TW1 |
80 |
mm |
154 |
130 |
8 |
11 |
|
inch |
6.06 |
5.12 |
|
0.43 |
||
|
TW3 |
100 |
mm |
174 |
150 |
8 |
14 |
|
inch |
6.85 |
5.91 |
|
0.55 |
||
|
TW5 |
125 |
mm |
204 |
176 |
8 |
14 |
|
inch |
8.03 |
6.93 |
|
0.55 |
||
|
TW7 |
150 |
mm |
240 |
210 |
12 |
14 |
|
inch |
9.45 |
8.27 |
|
0.55 |
|
T.T.M.A |
|
INCH |
ØD |
Øk |
n |
Ød |
|
2” |
mm |
114,3 |
95,3 |
6 |
11,1 |
|
inch |
4.50 |
3.75 |
0.44 |
||
|
3” |
mm |
142,9 |
123,8 |
8 |
11,1 |
|
inch |
5.63 |
4.87 |
0.44 |
||
|
4” |
mm |
168,3 |
149,2 |
8 |
11,1 |
|
inch |
6.63 |
5.87 |
0.44 |
||
|
5” |
mm |
196,9 |
177,8 |
12 |
11,1 |
|
inch |
7.75 |
7.00 |
0.44 |
||
|
6” |
mm |
228,6 |
206,4 |
12 |
11,1 |
|
inch |
9.00 |
8.13 |
0.44 |
||
|
8” |
mm |
276,2 |
257,2 |
16 |
11,1 |
|
inch |
10.87 |
10.13 |
0.44 |
Mounting instruction
When installing Mann Tek equipment to new pipe work, tanks, etc. ensure the system is free from debris that may be transferred through the coupling. Where the hose or loading arm assembly is the primary static dissipation or earth route, the electrical continuity value of the assembly shall be checked to ensure regulatory compliance. Special attention should be paid to the balancing of loading arms. The weight of the coupling plus transfer media should be taken into account at the specification stage. It is usual for loading arm balance settings to account of weight variations due to differences in the full / empty cycle.
The loading arm should be set to balance in the condition present at the time of connection. For example, should the loading arm be empty at the time of connection then it should be balanced in the empty condition.
The Mann-Tek product can be installed directly in the product line and is ready for use after
removing the transport protection. The installation is recommended as follows:
a. Remove the packaging and the flange protection
b. Check the coupling for damages before mounting.
c. To prevent damages during mounting a suitable wrench should be used for the intended bolts and nuts.
d. Ensure that the product line is empty and all valves are close
before you connect the coupling into the line.
e. Set in all bolts first and tighten them by hand. Then increase the tightening torque in 2 steps up to the
recommended value in the following table. Proceed every time according to the sequence shown in g.
f. Tightening torque1) for bolts:
|
Metric |
|
|
Size |
8.8 |
|
M8 |
24 Nm |
|
M10 |
50 Nm |
|
M12 |
85 Nm |
|
M16 |
210 Nm |
|
M20 |
410 Nm |
|
M22 |
550 Nm |
|
M24 |
700 Nm |
|
Inch Size A193 B7 |
|
|
5/16 -18 UNC |
16 lbf-ft |
|
3/8 -16 UNC |
29 lbf-ft |
|
1/2 -13 UNC |
70 lbf-ft |
|
5/8 -11 UNC |
139 lbf-ft |
|
3/4 -10 UNC |
243 lbf-ft |
|
7/8 -9 UNC |
389 lbf-ft |
|
1 -8 UNC |
582 lbf-ft |
4 Bolt Pattern 8 Bolt Pattern 12 Bolt Pattern
The start-up may take place only when the Mann-Tek product has been mounted as instructed and the necessary function tests and leak tests have been conducted by the approved authorities.
1) The torque forces recommended bases on a thread friction coefficient μ=0,14 and a standard flat seal
according to EN 1514-1
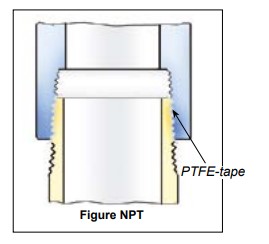
Sealing NPT threads can be an exasperating experience if certain techniques are not followed. The following tips will help alleviate many common problems in thread sealing:
1. Always use some type of sealant (tape or paste) and apply sealant to male thread only. If using a hydraulic sealant, allow sufficient curing time before system is pressurized.
2. When using tape sealant, wrap the threads in a clockwise motion starting at the first thread and, as layers are applied, work towards the imperfect (vanishing) thread. If the system that the connection being made to cannot tolerate foreign matter (i.e. air systems), leave the first thread exposed and apply the tape sealant as outlined above.
3. When using paste sealant, apply to threads with a brush, using the brush to work the sealant into the threads. Apply enough sealant to fill in all the threads all the way around.
4. When connecting one stainless steel part to another stainless steel part that will require future disassembly, use a thread sealant that is designed for stainless steel. This stainless steel thread sealant is also useful when connecting aluminium to aluminium that needs to be disconnected in the future. These two materials gall easily, and if the correct sealant is not used, it can be next to impossible to disassemble.
5. When connecting parts made of dissimilar metals (i.e. steel and aluminium), standard tape or paste sealant per forms satisfactor.
6. For sizes 2” and below, tape or paste performs satisfactory. When using thread tape, four wraps (covering all necessary threads) is usually sufficient.
7. For sizes 2½” and above, thread paste is recommended. If thread tape is used, eight wraps (covering all necessary threads) is usually sufficient. Apply more wraps if necessary.
8. For stubborn to seal threads, apply a normal coating of thread paste followed by a normal layer of thread tape.
9. For extremely stubborn to seal threads, apply a normal coating of thread paste followed by a single layer of gauze bandage followed by a normal layer of thread tape.
10. Over-tightening threads can be just as detrimental as insufficient tightening. For sizes 2” and below, hand tighten the components and, with a wrench, tighten 3 full turns. For sizes 2½” and above, hand tighten the components and, with a wrench, tighten 2 full turns.
Caution!
When this procedure is done, the connection becomes permanent. Extreme measures will be necessary to disconnect these components. All other measures to seal the threads should be explored prior to use of this technique.
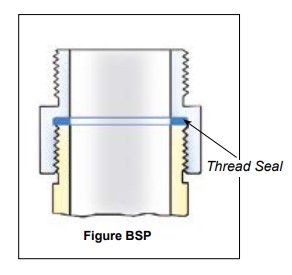
The threads are parallel with flat sealing surface.
This allows to use the full thread length for screwed-on parts. The largest possible transfer of force is guaranteed for short length. The thread seal behind the relief groove of the thread cannot drop out.
Simple screwing down, makes a safe connection. Subsequent tightening during operation is possible at any time. Change of seal and new assembly do not require any expert knowledge.
The European standardisations for hose assemblies require parallel threads with flat seals, because of the advantages.
|
weight ≈kg |
Thread BSP |
Materials Application |
Dimensions ≈ mm |
Product No |
||
|
D |
d |
s |
||||
|
0,001 |
BSP ½” |
PTFE ( Teflon®) white , massive continuously hard, universally resistant
Teflon® is a registered trademark of DuPont |
20 |
13 |
2 |
On request |
|
0,001 |
BSP 3/4” |
26 |
19 |
2 |
1498-06 |
|
|
0,002 |
BSP 1” |
33 |
24 |
2 |
1220-06 |
|
|
0,003 |
BSP 1 1/4” |
42 |
34 |
2 |
1536-06 |
|
|
0,003 |
BSP 1 ½” |
48 |
39 |
2 |
1196-06 |
|
|
0,004 |
BSP 2” |
60 |
49 |
2 |
1052-06 |
|
|
0,007 |
BSP 2 ½” |
76 |
63 |
2,5 |
1181-06 |
|
|
0,006 |
BSP 3” |
88 |
77 |
3 |
1110-06 |
|
|
0,009 |
BSP 4” |
114 |
100 |
3 |
1295-06 |
|
|
0,016 |
BSP 6” |
164 |
150 |
3 |
1963-06 |
|
|
0,001 |
BSP ½” |
Thermopac asbestos free, light hard. Especially for hot oils and hot bitumen up to 250º C and for hot water and saturated steam up to 25 bar. |
20 |
13 |
2 |
On request |
|
0,001 |
BSP 3/4” |
26 |
19 |
2 |
1498-25 |
|
|
0,002 |
BSP 1” |
33 |
24 |
2 |
1220-25 |
|
|
0,002 |
BSP 1 1/4” |
42 |
34 |
2 |
1536-25 |
|
|
0,003 |
BSP 1 ½” |
48 |
39 |
2 |
1196-25 |
|
|
0,004 |
BSP 2” |
60 |
49 |
2 |
1052-25 |
|
|
0,005 |
BSP 2 ½” |
76 |
63 |
3 |
1181-25 |
|
|
0,009 |
BSP 3” |
88 |
77 |
3 |
1110-25 |
|
|
0,013 |
BSP 4” |
114 |
100 |
3 |
1295-25 |
|
|
0,016 |
BSP 6” |
164 |
150 |
3 |
1963-25 |
|
|
0,001 |
BSP 1/2” |
FPM/FKM (Viton®) soft for aromatic hydrocarbons and hot oils.
Viton® is a registered trademark of DuPont |
20 |
13 |
2 |
On request |
|
0,001 |
BSP 3/4” |
26 |
19 |
2 |
1498-01 |
|
|
0,002 |
BSP 1” |
33 |
24 |
2 |
1220-01 |
|
|
0,002 |
BSP 1 1/4” |
42 |
34 |
2 |
1536-01 |
|
|
0,003 |
BSP 1 ½” |
48 |
39 |
2 |
1196-01 |
|
|
0,004 |
BSP 2” |
60 |
49 |
2 |
1052-01 |
|
|
0,006 |
BSP 2 ½” |
76 |
63 |
3 |
1181-01 |
|
|
0,008 |
BSP 3” |
88 |
77 |
3 |
1110-01 |
|
|
0,014 |
BSP 4” |
114 |
100 |
3 |
1295-01 |
|
|
0,016 |
BSP 6” |
164 |
150 |
3 |
1963-01 |
|
|
0,001 |
BSP 3/4” |
PUR (Vulkollan®) Flat seals type of polyurethane, hightly resitant to abrasion, non-toxic. Shore hardness=900 . For all petroleum based products and many solvents. Colour:Blue
Vulkollan® is a registe- red trademark of Bayer |
26 |
19 |
2 |
1498-09 |
|
0,001 |
BSP 1” |
33 |
24 |
2 |
1220-09 |
|
|
0,001 |
BSP 1 1/4” |
42 |
34 |
2 |
1536-09 |
|
|
0,002 |
BSP 1 ½ ” |
48 |
39 |
2 |
1196-09 |
|
|
0,003 |
BSP 1 3/4” |
54 |
44 |
2,5 |
On request |
|
|
0,003 |
BSP 2” |
60 |
49 |
2 |
1052-09 |
|
|
0,005 |
BSP 2 ½ ” |
76 |
63 |
2,5 |
1181-09 |
|
|
0,006 |
BSP 3” |
88 |
77 |
3 |
1110-09 |
|
|
0,010 |
BSP 3½” |
100 |
80 |
3 |
On request |
|
|
0,009 |
BSP 4” |
114 |
100 |
3 |
1295-09 |
|
|
0,012 |
BSP 5” ( No std) |
140 |
124 |
3 |
On request |
|
|
0,016 |
BSP 6” |
164 |
150 |
3 |
1963-09 |

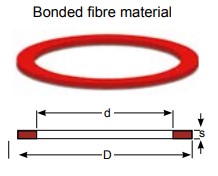
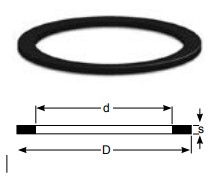
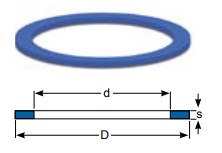
|
Flange standard / suitable for D d Øk Øh s |
|
DN 25 PN 10/16 |
108 |
78,5 |
91 |
4 x 6,5 |
2 |
- |
|
DN 32 PN 10/16 |
140 |
43 |
100 |
4 x 18 |
2 |
- |
|
DN 50 PN 6 |
140 |
61 |
110 |
4 x 15 |
2 |
- |
|
DN 50 TW 1 |
154 |
50 |
130 |
8 x 12 |
2 |
- |
|
DN 80 TW 1 |
154 |
90 |
130 |
8 x 12 |
2 |
- |
|
DN 50 PN 10/16 |
165 |
61 |
125 |
4 x 18 |
2 |
- |
|
DN 100 TW3 |
174 |
110 |
150 |
8 x 14 |
2 |
- |
|
DN 65 PN 10/16 |
185 |
76 |
145 |
4 x 18 |
2 |
- |
|
DN 80 PN 10/16 |
200 |
90 |
160 |
8 x 18 |
2 |
- |
|
DN 125 TW5 |
204 |
135 |
176 |
8 x 14 |
2 |
- |
|
DN 100 PN 10/16 |
220 |
115 |
180 |
8 x 18 |
2 |
- |
|
DN 150 TW7 |
240 |
160 |
210 |
12 x 14 |
2 |
- |
|
DN 125 PN 10/16 |
250 |
141 |
210 |
8 x 18 |
2 |
- |
|
DN 150 PN 10/16 |
280 |
169 |
240 |
8 x 22 |
2 |
- |
|
DN 200 PN 10 |
340 |
220 |
295 |
8 x 22 |
2 |
- |
|
DN 200 PN 16 |
340 |
220 |
295 |
12 x 22 |
2 |
- |
Product No- ON REQUEST

MATERIAL:
ELAPAC- FD is a three component mixture, made of RUBBER (NBR) vulcanised, for the adhesion and resistance to kinking.
CORK for compressibility and sealing capability. When tightening the flange seal does not move towards the outer or inner edge of the sealing faces.The flange
seal does not ”settle,” and can be re-used in most cases.
FIBRES give the material the necessary rigidity and the stability to insert flange seals into narrow gaps from the side. The values for swelling are considerably
lower for fibre reinforced mixtures than for plain rubber seals.
Further advantages: No leaching out of softening agents. No shrinking or hardening through drying. No influence on or discoloration of media. No hardening at temperature range of -25 o up to +70o Celsius. No sticking on flange. Additional ”adhesives” are not necessary. – Therefore good reusability. A high adaptability, where flange seals should still have good flexibility to avoid pipe fractures or simple sealing materials because little or no force can be used to tighten the joint. Not suitable for use as thread seal, because the material is too soft and does not have enough lateral strength, this allows the medium to attack the seal material. Also not suitable for applications where the flange seal is only squashed on 2 mm to 3 mm of the total width. Care should be taken not to squash the material to much especially the 2 mm material, if in doubt please use the 3 mm material.
GAS IMPERMEABILITY :
Due to the fibre content of ELAPAC; gas permeability is to be expected when using seals with narrow width – especially at high vacuum operation.
APPROVALS:
Approved as flange sealing material for all fuels and lubricants by the German military and the major oil companies for tank trucks, refineries and aircraft refuellers. Approved in 3 mm thickness by the German railway (Mat. No. 150.309). ELAPAC-FD meets the DIN 28 463.
RESISTANCE:
The details refer to fitted flange seals. Only the inner rim of the flange seal is in contact with the medium. In the event of a possible attack this would only result in low penetration and the use is still possible. If the flange seal is completely immerged in the medium during laboratory tests, swelling and loss of stability is of course higher. If the resistance of ELAPAC is not sufficient but good compressibility is required, we offer the special design ”TM” seal which is PTFE encapsulated. Application of foodstuffs: ELAPAC-FD is only suitable with PTFE-cover, otherwise mixture particles can influence the quality of the foodstuffs.
APPLICATION: As an elastic flange seal for tank truck and tank plant construction etc., where rough sealing surfaces require.
TECHNICAL DATA:
hardness, Shore A 86 ± 3
tensile strength longitudinal 10 N/mm2 lateral 4,5
elongation at break longitudinal 15 N/mm2 lateral
compressibility 75 %
recovery 90 %
compression set 24h, 700 C 40 %
tear resistance longitudinal 7 N/mm2 lat
working pressure maximal 25 bar
colour blue
marking print
|
Designation |
Trade name |
ISO 1629 |
ASTM 1418 |
Temp Range oC |
Field of Application |
|
|
Nitrile Butadiene Rubber |
Buna N® Europrene N® Hycar® Nipol N® Perbunan N® |
NBR |
NBR |
-45 |
110 |
Standard material for hydraulics and pneumatics. Mineral oil-based hydralic fluids, animal and vegeta- ble oils and fats. Flame retardant liquids. Aliphatic hydrocarbons (prophane, butane, petrol). Silicone oils and greases. Water up to 80Cº. Bio oils made from synthetic esters and vegetable oils |
|
Ethylene- Propylene-Diene Rubber |
Dutral Keltan® Vistalon® Buna AP® |
EPDM |
EPDM |
-55 |
120 |
Hot water, vapour, brake fluids, detergents. Alcohols, ketons, engine coolants, flame retardant phosphate-ba- sed liquids, organic and inorganic acids and bases. Not resistent to mineral oils |
|
Fluoroelastomer |
Fluorel® Technoflon® Viton® |
FPM |
FKM |
-20 |
200 |
Mineral oil and greases. Aliphatic, aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons, petrol, 99 octan petrol, diesel fuels, flame retardant phosphatebased liquids. Silicone oils and greases acids, Iyes |
|
Fluorosilicone Elastomer |
- |
MFQ |
FVMQ |
-60 |
200 |
Mineral oils, fuels. lubricant on Di-Ester basis, hot air. |
|
Silicone |
Silastic® Silopren® |
MVQ |
VMQ |
-60 |
200 |
Mineral oils, fuels. lubricant on Di-Ester basis, hot air. |
|
Hydrogenated Nitrile- Butadiene Rubber |
Therban® Tornac® Zetpol® |
HNBR** |
HNBR** |
-35 |
120 |
Mineral oil-based hydralic fluids, animal and vegetable fats, aliphatic hydrocarbons, diesel fuels, ozone, sour gas, dilute acids and bases Mineral oil-based hydralic fluids, animal and vegetable fats, aliphatic hy- drocarbons, diesel fuels, ozone, sour gas, dilute acids and bases |
|
Butyl Rubber |
Exxon Butyl® Polysar Butyl® |
IIR |
IIR |
-55 |
100 |
Butyl is a copolymer of isobutylene and isoprene. It has largely been replaced by ethylene propylene for O-ring usage. Butyl is resistant to the same fluid types as ethylenepropylene and except for resistance to gas permeation, it is somewhat inferior to ethylene-propy- lene for O-ring service. Excellent weather resistance, and gas permeation resistance. Poor petroleum oil and fuel resistance. |
|
Perfluorinated Elastomer |
CHEMRAZ® Kalrez® PERLAST® |
FFPM |
FFPM |
-40 |
260 |
Best chemical resistance of all elastomers, including organic acids, f.i. acetic acid, benzoic acid, formic acid |
|
Chloroprene Rubber |
Baypren® Neoprene® |
CR |
CR |
-40 |
120 |
Resistant to refrigerants, ammonia, carbon dioxide, freon(R12,R13,R21,R22,R113-R115), silicone oils, water, oxygen(low-pres.), bleaches, coustic soda, alcohols, chlorine, ozone, castor oil and veg. oils. Low resistance to mineral oils! |
|
Polyester / Polyether Urethane Rubber |
Adiprene® Urepan® Vulkollan® Desmopan® |
AU EU PUR |
AU EU |
-40 |
100 |
Mineral oils and greases, oxygen, ozone. HFA and HFB fluids, air. Not resistant in esters, aliphatic, aromatic and chlorina- ted hydrocarbons, concentrated acids and lyes, water above +50ºC. |
|
Polytetrafluoroethylene |
Teflon® |
PTFE |
PTFE |
-200 |
260 |
PTFE is used wherever the chemical and thermal re- sistance of the normal elastomer is no longer sufficient. These are primarily applications in the chemical indu- stry, foodstuffs industry, pharmaceuticals and medical technology. PTFE are used only as static seals, e.g. on flange connections, on covers, .etc. |
|
Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene |
Teflon FEP® |
FEP/MVQ |
FEP/VMQ |
-60 |
200 |
FEP is used wherever the chemical and thermal resis- tance of the normal elastomer is no longer sufficient. These are primarily applications in the chemical indu- stry, foodstuffs industry, pharmaceuticals and medical technology. |
|
FEP/FPM |
FEP/FKM |
-20 |
200 |
|||
|
Perflouralkoxy |
Teflon PFA® |
PFA/MVQ |
PFA/VMQ |
-60 |
250 |
PFA is used wherever the chemical and thermal resis- tance of the normal elastomer is no longer sufficient. These are primarily applications in the chemical indu- stry, foodstuffs industry, pharmaceuticals and medical technology. |
|
PFA/FPM |
PFA/FKM |
-20 |
250 |
|||
|
Tetrafluoroethylene- Propylene Copolymer Elastomer |
Aflas® |
—- |
TFE / P** |
-25 |
200 |
Mineral oils and greases, brake fluids, fuels, alcohols, heat transfer media, oils. amines, acids, bases |
Didn't find the right Swivel Joints?
Fill in the form below, and we'll assist you further!
Curious about our blog? Check out all our items here!
Contact us here